关于firewalld和iptables
先说结论:
firewalld无法控制来自本地的流量iptables可以控制来自本地的流量iptables默认对ipv4生效,ip6tables对ipv6生效telnet命令默认会将localhost被解析成::1nmap会按照/etc/hosts将localhost解析成127.0.0.1ping在不通的操作系统下localhost的解析效果也不一样, centos中解析为127.0.0.1debian12 中是::1
环境介绍
| Feature | Server A | Server B |
|---|---|---|
| OS: | CentOS 7.9 | Debian 12 |
| ARCH: | KVM x86-64 | KVM x86-64 |
| IP: | 192.168.1.201 |
192.168.1.28 |
| Docker Remote Port: | 2376 | 2376 |
| Firewalld Version: | v0.6.3 | v1.3.3 |
两台服务器默认 iptables为空, firewalld 为空;
默认情况下, iptables 允许放行,firewalld 拒绝;
两台服务器的docker端口均默认监听在tcp6上
端口测试脚本:
|
测试一
1.1 CentOS:

1.2 Debian:

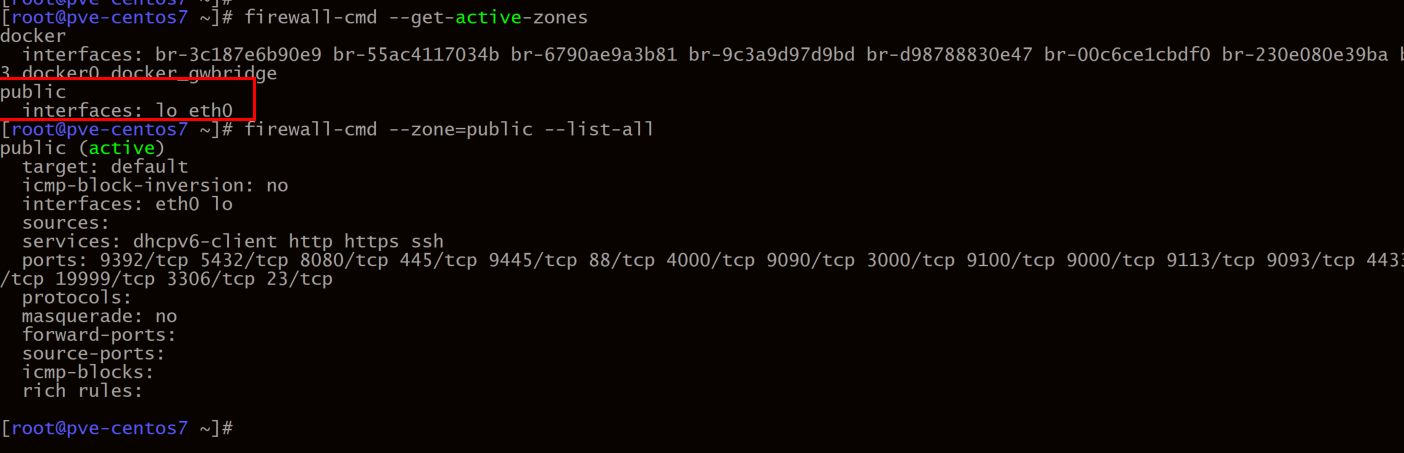
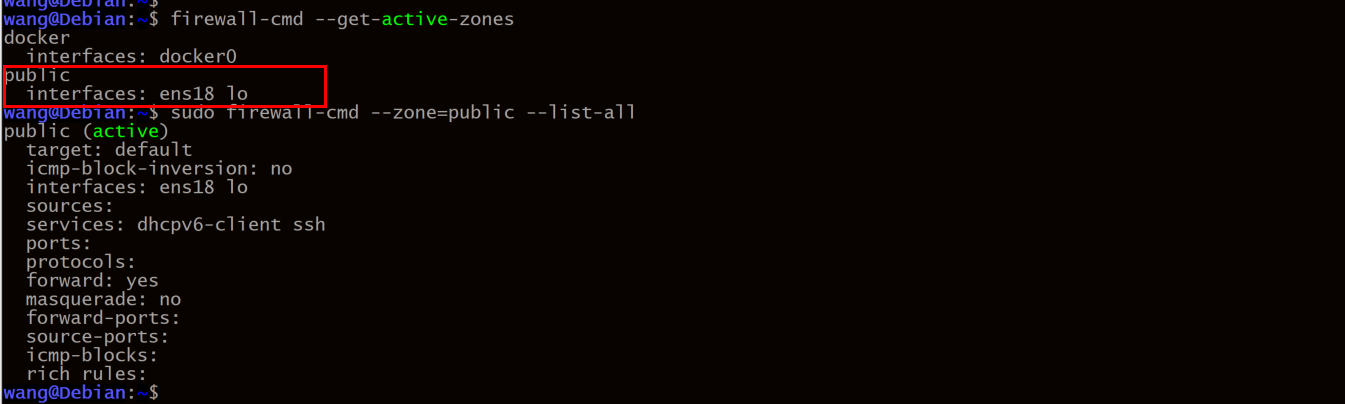
结论: firewalld 并不能控制来自本地的流量,即使public的接口里添加了 lo
测试二
两台服务器都添加 iptables 规则后再继续执行脚本测试
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 2376 -j DROP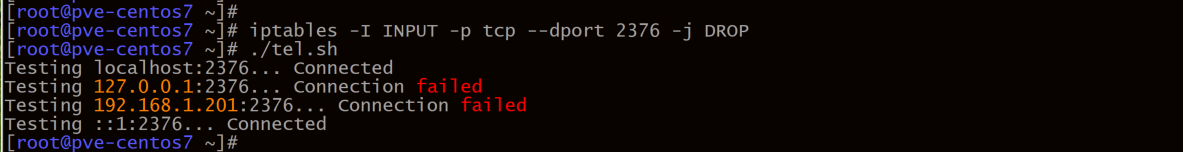
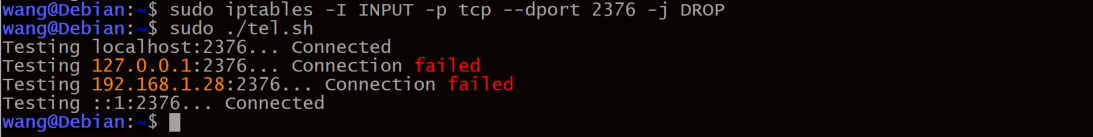
脚本省略了命令行的输出, 用命令测试一下 telnet localhost 2376
发现两台服务器解析localhost的时候默认解析成 ::1
结论:iptables 可以阻止来自本地的流量,包括环回接口loiptables 默认只处理 ipv4 的流量, ipv6的流量使用 ip6tableslocalhost默认会解析成::1